Tel: +33 (0) 1 47 20 40 07
86 Avenue Foch, 75116 Paris France
Wednesday, thursday and Friday,
A breast implant consists of a silicone elastomer shell (solid silicone), usually filled with physiological saline (water and salt) or silicone gel.
The shape of the implant is generally round, but in some cases so-called “anatomical” implants having a teardrop shape can be used.
The implant shell can be smooth or rough (textured), in this case reducing the risk of shell formation around the implant.

Smooth walled silicone gel pre-filled implant
![]()
Round shape prosthesis on the left and anatomical shape on the right
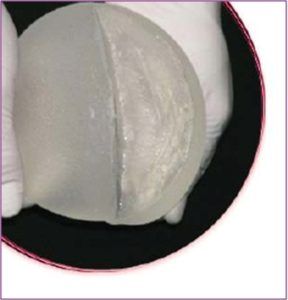
COHESIVE silicone gel pre-filled prosthesis
The history of breast augmentation is quite old.
It begins at the end of the 19th century with the German CZERNY who fills a breast depression left by the removal of an adenoma (benign tumor) and a lipoma (benign fatty tumor) taken from the lumbar region.
Subsequently, three methods will be used in the 20th century, combining hopes, spectacular successes and sometimes disappointments:
Intra or retro-mammary injections of different substances (liquid silicone, microbead, etc.),
In 1963, two Americans, doctors CRONIN and GEROW, presented a new type of prosthesis at the International Congress of Plastic Surgery in Washington.
This is a thick silicone pouch containing a silicone gel. Dacron patches (rough surface) are placed on the posterior surface of the implants in order to limit their displacement. The first breast prosthesis was born.
The success of silicone prostheses is immediate and considerable.
In France, it is Dr Jacques Faivre who introduces the Japanese silicone prostheses of Dr Akyama.
It replaces injections with a silicone bag into which silicone gel can be injected during the procedure.
In 1965, Doctor Arion, a French surgeon, presented a silicone elastomer prosthesis that was filled with a liquid (dextran or polyvinyl pirolidone at 40%). The injection is done through a pipe connected to the prosthesis and closed by a plug: it is the first inflatable prosthesis.
Later, this inflation hose will be replaced by a diaphragm valve. Today, this valve is still used for inflatable prostheses.
In the 1970s, plastic surgeons essentially had 2 types of breast implants: Silicone Cronin prostheses and Arion inflatable prostheses.
All breast implants are made of a silicone elastomer shell (solid silicone) which is in contact with the body.
The implant is said to be pre-filled when the filling product has been incorporated at the factory (silicone gel or physiological serum), its volume is therefore set by the manufacturer.
In contrast, physiological saline inflatable prostheses are filled by the surgeon who can adapt, within a certain limit, the volume of the prosthesis during the operation.
Other filler materials such as soybean oil, PVP or hydrogel have also been tried.
The first prostheses were round and are still the most widely used today, their profile projection and base vary according to the manufacturers. In recent years, there have been so-called “anatomical” implants in the shape of a drop of water, the implantation of which may be more natural, in particular in breast reconstruction.
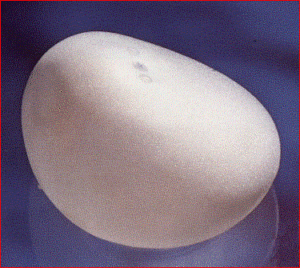
Anatomical textured inflatable implant
In cosmetic surgery, breast augmentation with prostheses often gives patients a feeling of femininity. There is a change in clothing behavior with the use of necklines replacing the wearing of a “chest shield”.
Whatever the indication, the psychological benefit is always present and it is necessary for obtaining a good result. However, the morphological change can sometimes be poorly accepted at first because it involves the implantation of a foreign body that the patient will have to integrate into her body.
In breast reconstruction after cancer, the psychological benefits are very important and this is true for any method of reconstruction.
For the patient, it is the possibility to no longer have to wear an external prosthesis, being able to dress differently by wearing low necklines again, finding a body image close to normal and partly forgetting how their body was mutilated, a constant reminder of the disease.
The breast prosthesis corrects: the asymmetry of the breasts after removal or the failure / absence of development of one or both breasts in some women.
Finally, there is the possibility of no longer using cover-ups such as: padded bras, Wonderbra® …
Many women who have had a mastectomy claim that the prosthesis has helped them reduce shoulder pain and poor posture used to hide their prosthesis.
The thorax is sometimes hypersensitive after a mastectomy, irritated by the external prosthesis, especially after radiotherapy. In this case, the breast implant can play an additional role of covering between the skin and the chest wall. Breast reconstruction also makes it possible to correct the after effects of previous local treatments.
There is no age limit for fitting a breast prosthesis. In plastic surgery, a breast prosthesis can be implanted after puberty, especially in the case of significant breast asymmetry.
In young girls, hormonal changes and the possible use of a contraceptive are factors that can change the size of the breasts. It is best to wait until the end of puberty to appreciate the volume of the breasts.
After cancer, reconstruction of the breast with prosthesis remains the simplest and fastest means of reconstruction, in the majority of cases. There is no age limit, only the general condition of the patient allowing general anesthesia is the limiting factor.
In cosmetic surgery, you have to discuss the desired breast size with your surgeon. The latter will be able to advise you on an implant volume adapted to your morphology.
It is useful for patients to use a magazine photo to indicate the desired breast volume to the surgeon.
Today, it is possible for the surgeon to simulate breast augmentation using so-called morphing software.
Currently, in France, prostheses pre-filled with silicone gel have been authorized since February 2001. There was a ban (moratorium) between 1996 and 2001 which was lifted on this type of implant.
However, the use of other types of implants (hydrogel, soybean oil, etc.) is still prohibited pending further scientific information on their safety.
Since June 14, 1998, CE marking has been compulsory for all medical devices. Any product obtaining its CE marking in one of the countries of the European Union can be marketed throughout Europe as soon as this has been obtained.
Thus in France, two types of implants are marketed; inflatable prostheses with physiological serum and prostheses pre-filled with silicone gel.
In the United States, it is also possible to implant pre-filled silicone gel prostheses, provided the patient agrees to participate in a study protocol approved by the FDA (US Department of Health). These protocols are conducted by manufacturers of implants authorized by the FDA. However, it is not possible, in the case of a first cosmetic implantation, to have silicone gel implants.
Authorizations are possible for breast reconstruction after cancer, in the event of hypoplasia (insufficient organ development), unilateral agenesis (total absence of organ development) or in patients already with gel implants who require a replacement.
In other countries of the European community, there is no limitation on the type of breast implant used.
To date, it is impossible to scientifically state that one implant is better or worse than another for the health of patients.
The manufacturing standards are strict and applicable to all manufacturers.
However, like any industrial process, the experience of some laboratories works in their favor. So, some surgeons prefer to use a single brand of implant with which they have experience.
Silicone has been used since 1950 as an implantable material. It is considered to be the best tolerated biomaterial because it is non-allergenic and inert.
Silicone molecules are introduced into the human body from birth. It is estimated that approximately 6 grams of silicone is present in the body of an adult.
Silicones are used as lubricants for needles, syringes and surgical instruments, but also as defoamer in glues, non-stick in certain dressings, but especially in cosmetology in certain eyeshadows. They are found in baby pacifiers, as well as in sunscreens, lipsticks, deodorants and many medicines.
Silicone has been blamed for triggering autoimmune diseases in some people. Due to the considerable number of women with breast implants (estimated at more than 10 million), it is normal to observe in these women the association of certain pathologies.
Today, there is no tangible scientifically recognized evidence of an increased risk of autoimmune disease in prosthesis pre-filled with silicone gel.
Yes, it is now possible, regardless of the indication (aesthetic or restorative) to have silicone gel prostheses. The new silicone gel is said to be Cohesive and will not leak if it breaks. it gives a rendering close to a normal breast and has a much longer lifespan than implants filled with serum.
Il n’existe, à ce jour, aucun élément probant permettant de penser que le transfert de graisse pourrait favoriser l’apparition d’un cancer du sein. En revanche, il n’en empêchera pas la survenue, si celui-ci devait apparaître.
La patiente a en effet son propre risque de survenue d’un cancer du sein, qui dépend notamment de son âge (risque évalué à un risque sur 218 avant 40 ans, et un risque sur 40 entre 50 et 59 ans), de ses antécédents familiaux, de sa densité mammaire. Elle doit aussi comprendre que toutes les précautions doivent être prises pour limiter le risque de coïncidence entre la survenue d’un cancer et le lipomodelage (bilan strict fait avant l’intervention par un radiologue spécialisé en imagerie du sein; bilan strict à 1 an, puis répété à 2 ans, voire 3 ans). Dans cet esprit, la patiente demandant un lipomodelage des seins, s’engage à faire réaliser le bilan pré-opératoire d’imagerie du sein (mammographie, échographie) et surtout s’engage à faire réaliser les examens de référence (mammographie, échographie) à 1 an, 2 ans, voire 3 ans en fonction des recommandations du radiologue spécialisé.
Enfin, il faut savoir que seul le recul dans le temps apportera la certitude absolue qu’un tel traitement ne peut favoriser ou être à l’origine d’une quelconque pathologie mammaire. A cet égard, la SOFCPRE recommande que la patiente s’engage à faire réaliser un bilan d’imagerie de référence un an après cette intervention, si possible par le même radiologue, puis à rester sous surveillance médicale régulière.
Il existe une cicatrice autour de l’aréole, une cicatrice verticale et une cicatrice dans le sillon sous le sein réalisant un T inversé ou une ancre de marine. Dans les cas de petite hypertrophie, la cicatrice dans le sillon peut être évitée, on parle de technique Verticale.
Le remodelage des seins doit tenir compte de la taille de la patiente, de l’épaisseur et de la largeur de son buste afin de prévoir un volume en harmonie avec sa silhouette. L’intervention a pour but de rééquilibrer les volumes tout en redonnant au mamelon et à l’aréole un emplacement naturel.
Il est toujours difficile de répondre à cette question car chaque cas est différent. On peut estimer qu’une patiente qui a une poitrine de 100 D aura après l’intervention une poitrine de 95 B ou C car son tour de thorax ne varie pas et seul le volume mammaire change.
L’allaitement reste le plus souvent possible après une plastie mammaire. Dans les cas de très grande hypertrophie (gigantomastie) on doit employer des techniques qui ne permettent pas l’allaitement secondaire car les aréoles et les mamelons sont greffés. On réserve ces interventions aux patientes ne désirant pas allaiter.
Tel: +33 (0) 1 47 20 40 07
86 Avenue Foch, 75116 Paris France
Wednesday, thursday and Friday,
Centre Ville: Clinique CLEAGE. Tel : +41 22 368 55 55
5, Place du Molard, 1204 Genève, Suisse
Vesenaz: : Clinique My Beauty. Rdv : +41 22 750 05 05 43, Route de Thonon 1222 Vesenaz, Suisse
Hours of operation may vary. If an urgent appointment is needed outside of these hours, please contact us for confirmation.